Veno Occlusive Disease Symptoms
Veno occlusive disease symptoms. These patients present with nonspecific symptoms including dyspnea exercise intolerance and weakness. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. Most people have mild to moderate VOD.
Fluid retention in abdomen or ascites. Coppell JA Richardson PG Soiffer R et al. The clinical picture is characterized by painful hepatomegaly jaundice and fluid retention that manifests by weight gain edemas and ascites.
Symptoms may include any of the following. There are two techniques available to confirm. The symptoms of hepatic veno-occlusive disease may be sudden in onset as the liver gets enlarged and becomes tender.
SOS can present in an acute subacute or chronic form usually with abdominal pain and swelling with evidence of portal. Read more about Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Complications Causes and Prognosis. Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease is a rare subcategory of pulmonary arterial hypertension WHO Group 1.
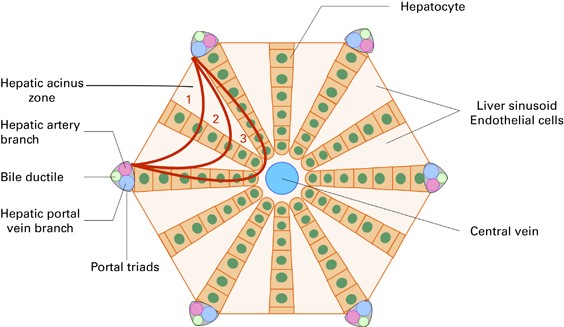
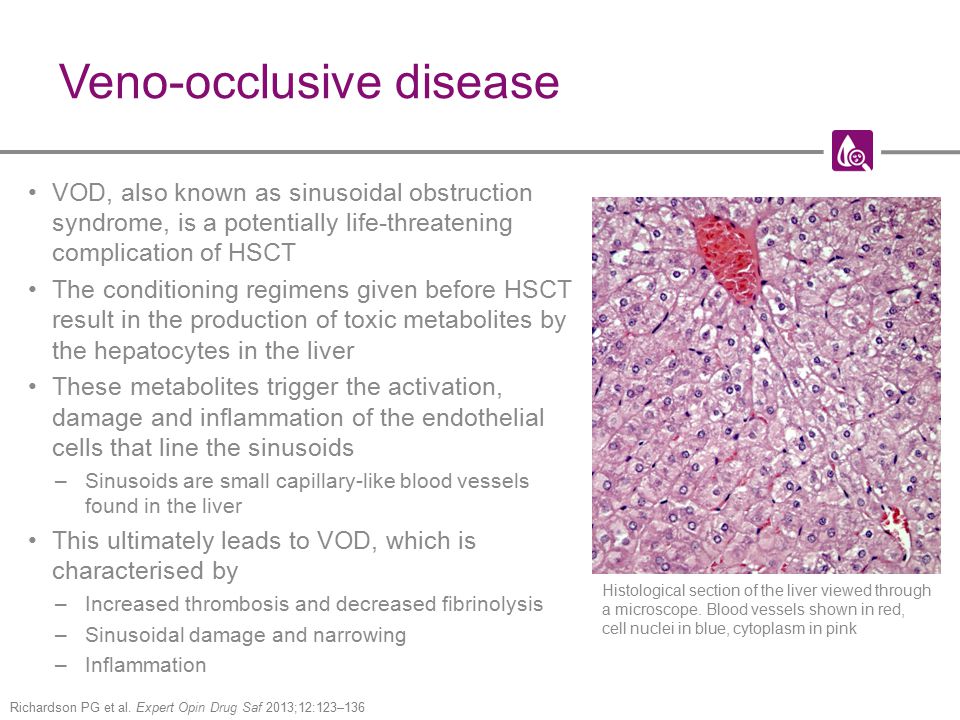
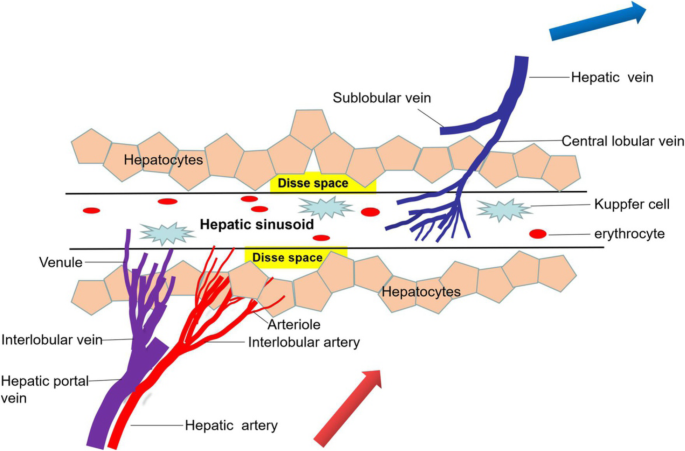
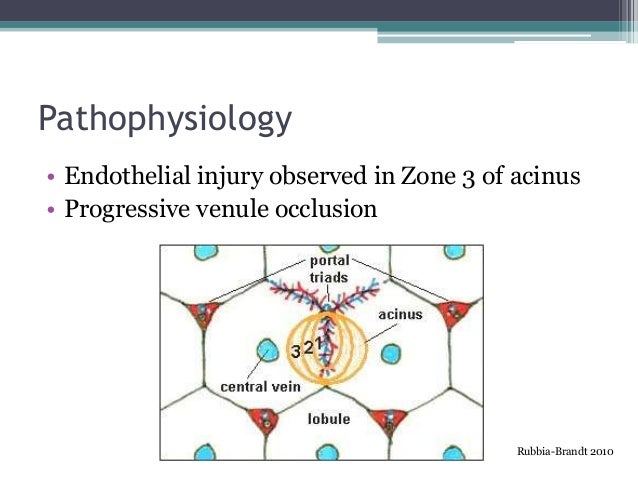
Symptoms include hyperbilirubinemia painful hepatomegaly and ascites. Liver tenderness under the ribs on the right side of the body ascites. The clinical syndrome of liver toxicity commonly called veno-occlusive disease that results from cytoreductive therapy before bone marrow transplant is strongly correlated with a constellation of histological lesions involving structures in zone 3 of the liver acinus and the hepatic venules into which sinusoidal blood flows.
VOD may also be referred to as sinusoidal obstruction syndrome or SOS by the transplant team. Preventing and managing VOD. There is fluid accumulation with swelling of the abdomen.
Signs and symptoms of VOD. The disease is poorly understood and difficult to diagnose.
VOD begins in the liver and can quickly affect other vital organs most notably the kidneys and lungs.
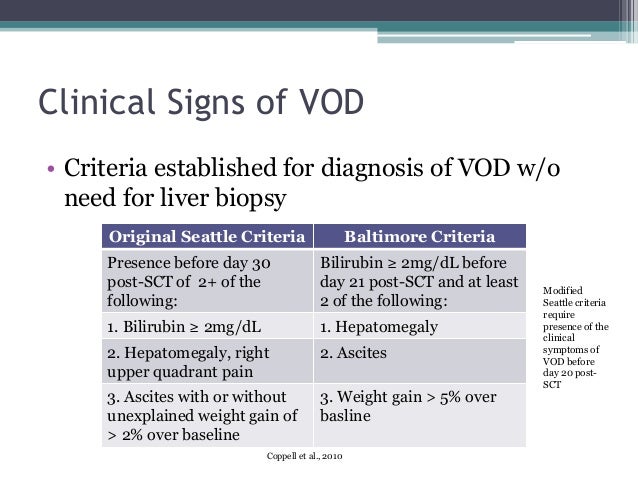
Clinical signs and symptoms of veno-occlusive disease include hepatomegaly right upper quadrant pain ascites fluid retention weight gain and hyperbilirubinemia usually developing by. The symptoms of acute hepatic veno-occlusive disease are. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease VOD is a complication that affects the liver and can occur following stem-cell transplant. Some of the symptoms listed may be signs of other problems with your SCT such as graft versus host disease or infection. Pain and tenderness in the abdomen especially on the upper right side due to swelling of the liver known as hepatomegaly Rapid weight gain compared to your weight when you started the transplant treatment. Difficulty breathing while lying flat. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease following stem cell transplantation. Liver tenderness under the ribs on the right side of the body ascites. Hepatic insufficiency manifesting as coagulopathy and hepatic encephalopathy may occur.
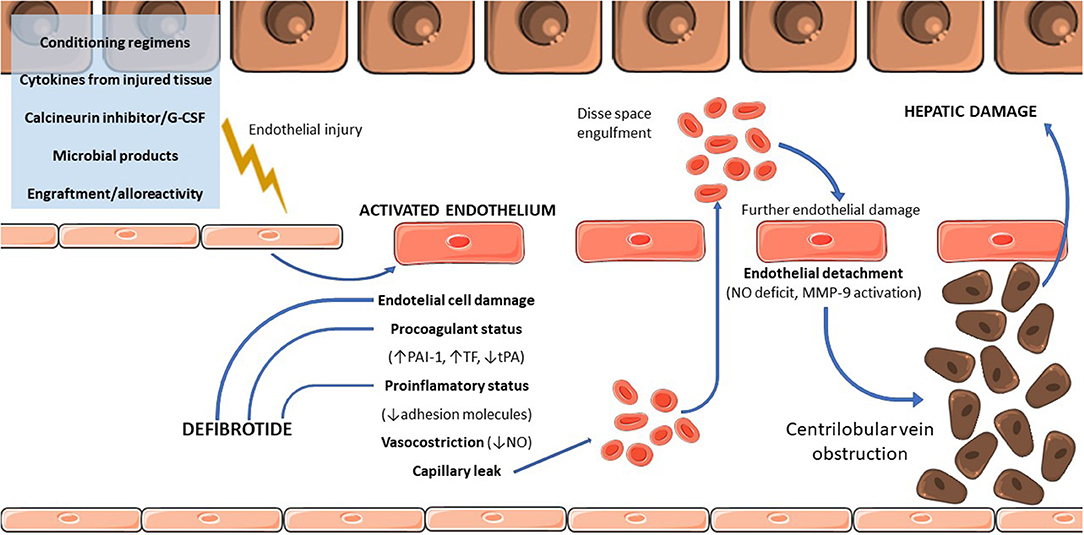
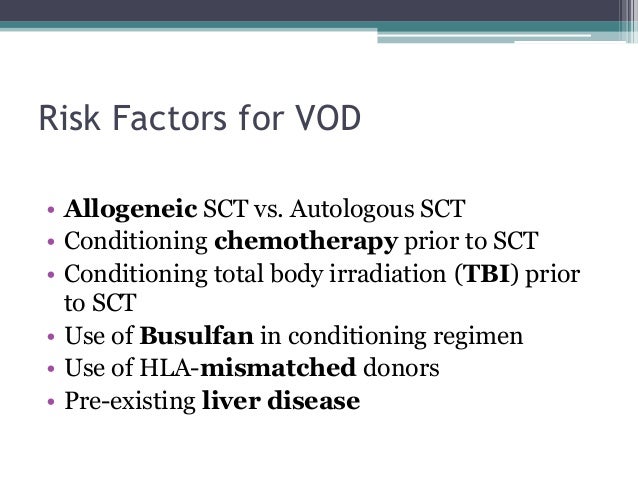
Various investigations may be needed to make an accurate diagnosis. The drug defibrotide Prociclide may be used to prevent or treat VOD. SOS also known as veno-occlusive disease VOD occurs as a result of cytoreductive therapy prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation HSCT following oxaliplatin-containing adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy for colorectal carcinoma metastatic to the liver and treated by partial hepatectomy in patients taking pyrrolizidine alkaloid-containing herbal remedies and in other particular settings such as the autosomal recessive condition of veno-occlusive disease. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome SOS previously known as veno-occlusive disease VOD is a distinctive and potentially fatal form of hepatic injury that occurs predominantly if not only after drug or toxin exposure. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease following stem cell transplantation. Fluid retention in abdomen or ascites. Increased pressure in the neck veins.


































Post a Comment for "Veno Occlusive Disease Symptoms"