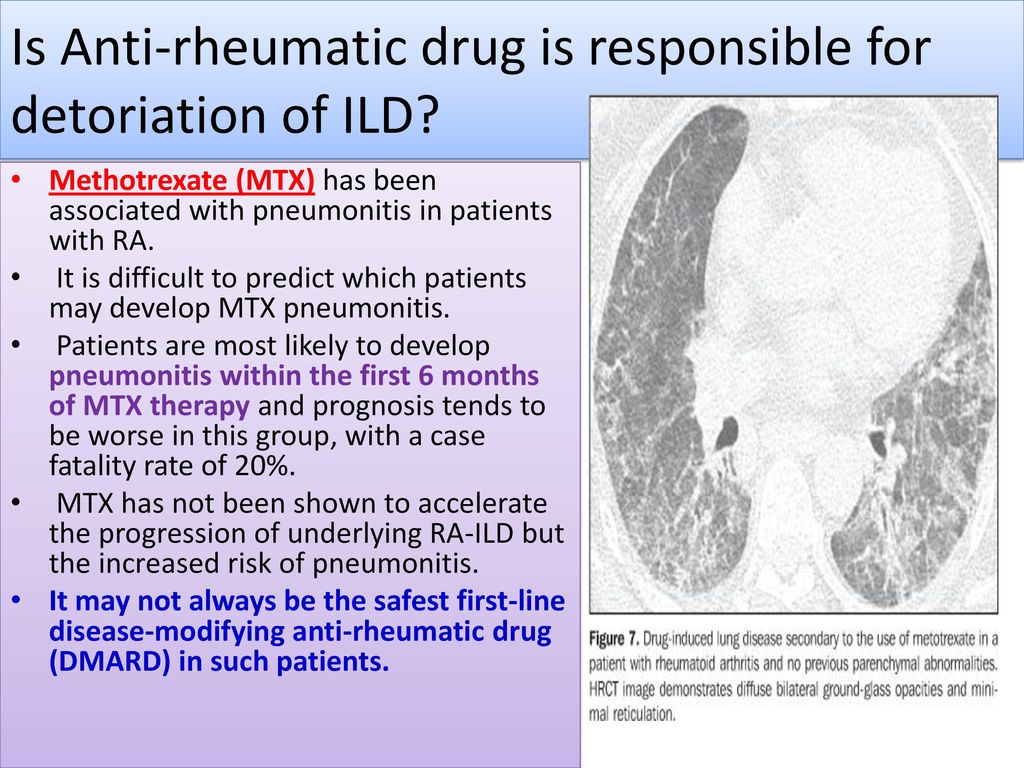
Methotrexate Interstitial Lung Disease
Methotrexate interstitial lung disease. For years standard medication with Methotrexate MTX has been suspected of. We aimed to evaluate the association of prior MTX use with development of RA-ILD. The aim is to evaluate the published evidence on whether methotrexate MTX use causes progressive fibrotic interstitial lung disease fILD.
Systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials 2015 R. BIRMINGHAM ENGLAND Data from two early RA inception cohorts provide reassurance that methotrexate does not cause interstitial lung disease and suggest that treatment with methotrexate might even be protective. For years standard medication with Methotrexate MTX has been suspected of either.
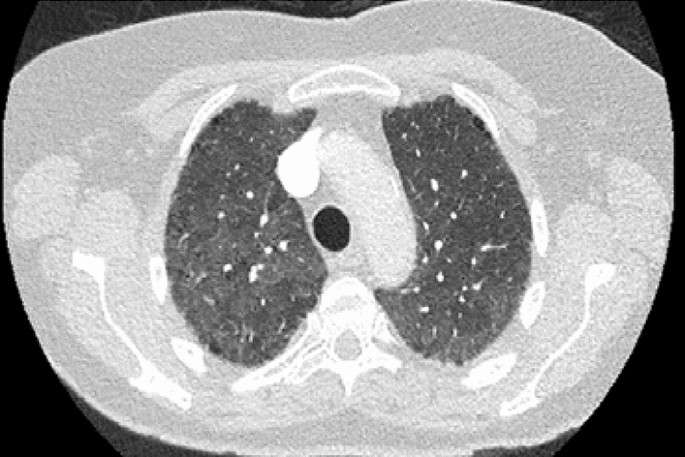
Whether MTX exposure increases the risk of ILD in patients with RA is disputed. Methotrexate has frequently been implicated as a causative agent in interstitial lung disease. Patients with RA have an elevated risk of interstitial lung disease ILD but methotrexate does not accentuate that risk and may in fact be protective new.
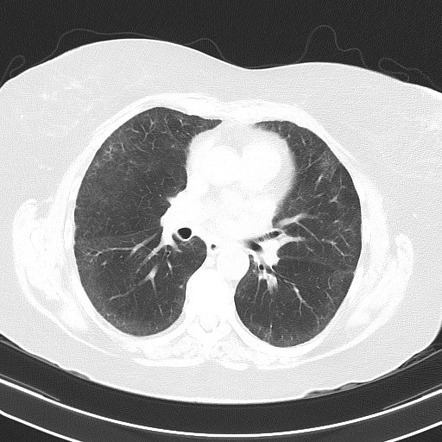
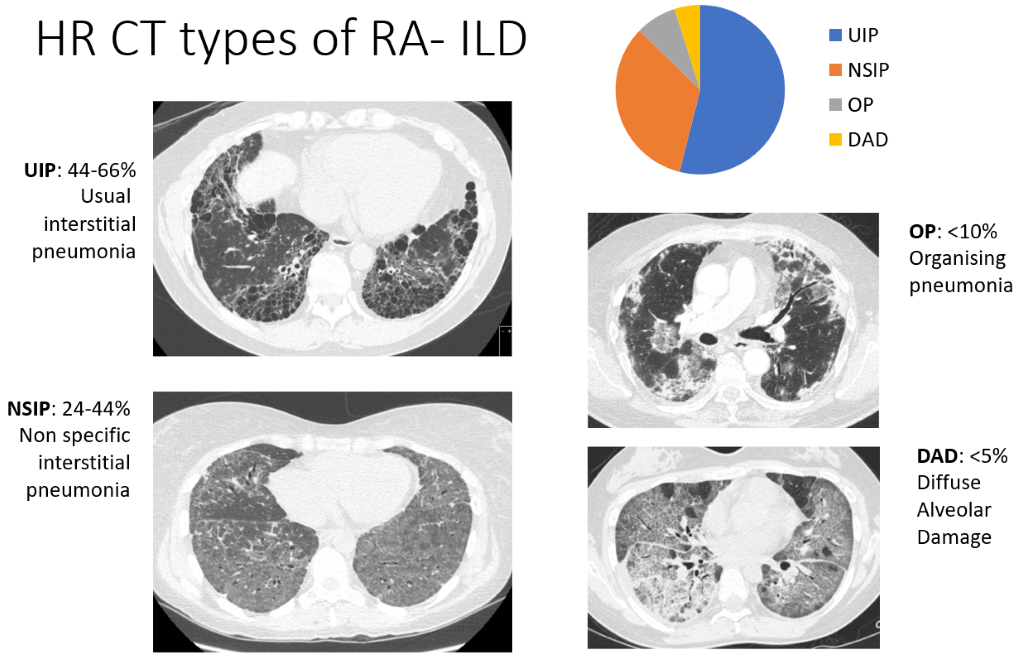
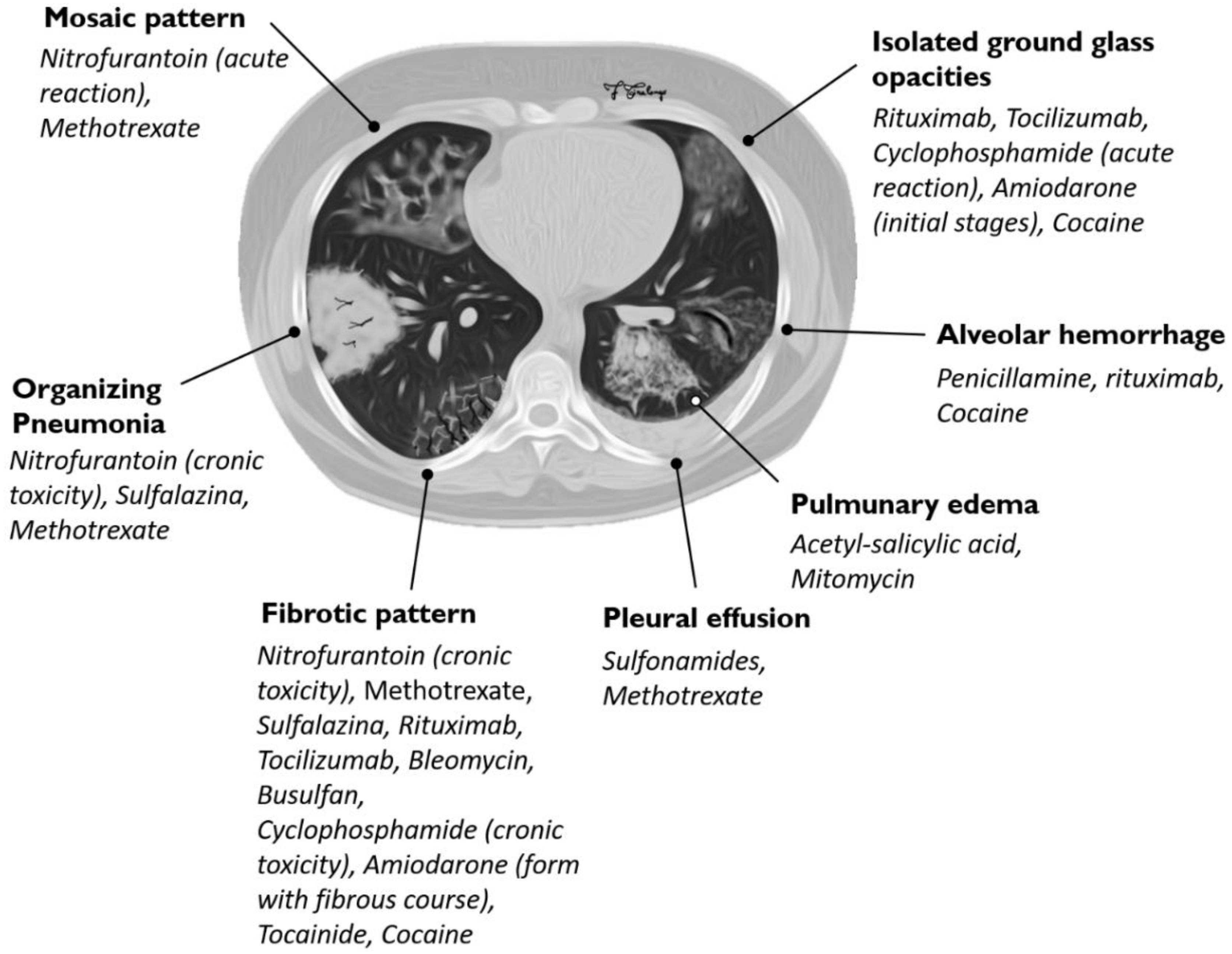
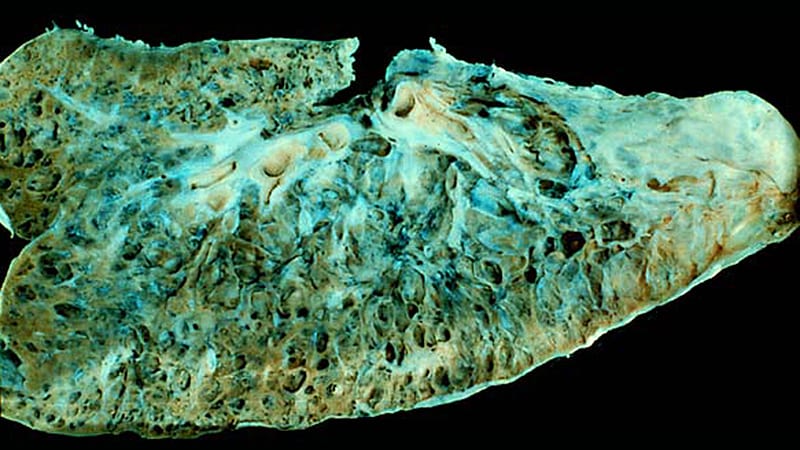
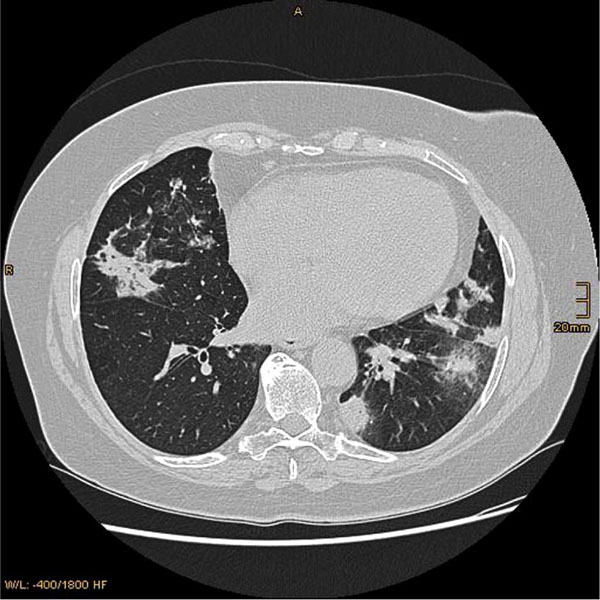
The role of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease Much has been made of the association between MTX and RA-ILD over the past few decades. The evidence for a cause and effect relationship in modern populations is contentious but critically important. There can be several manifestations of methotrexate-related lung changes.
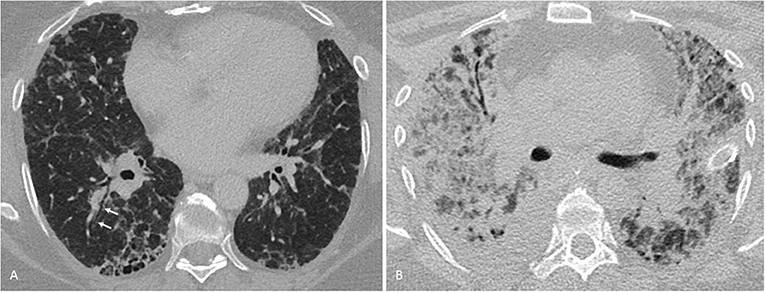
Fibrotic disease organizing pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia. Methotrexate is commonly prescribed for a variety of diseases including rheumatoid arthritis. However it has long been implicated as a causative agent in lung disease.
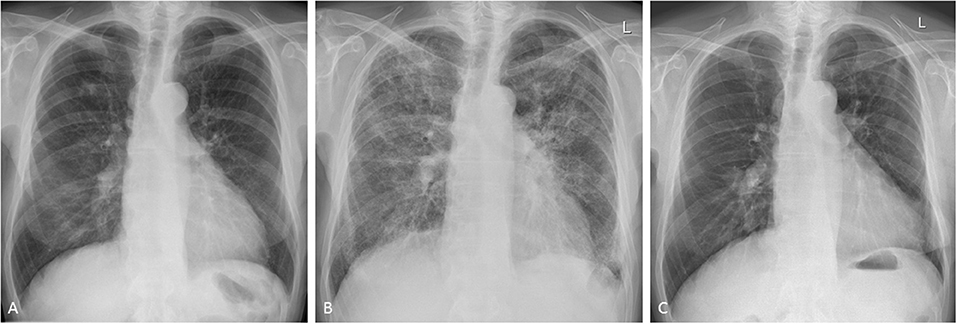
Methotrexate MTX is a commonly used drug for inflammatory joint diseases. Question addressed by the study Methotrexate MTX is a key anchor drug for rheumatoid arthritis RA management. Fibrotic interstitial lung disease ILD is a common complication of RA.
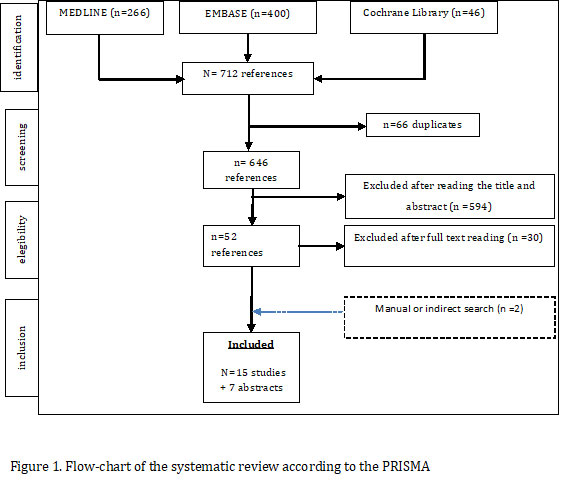
Organizing pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia or BOOP acute. A systematic review SR has been carried out using the PRISMA methodology 2 in order to determine the extent of involvement of MTX in DILD.
There can be several manifestations of methotrexate-related lung changes.
We aimed to evaluate the association of prior MTX use with development of RA-ILD. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis RA often suffer from what is referred to as interstitial lung disease ILD. BIRMINGHAM ENGLAND Data from two early RA inception cohorts provide reassurance that methotrexate does not cause interstitial lung disease and suggest that treatment with methotrexate might even be protective. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis RA often suffer from what is referred to as interstitial lung disease ILD. However it has long been implicated as a causative agent in lung disease. Methotrexate use and risk of lung disease in psoriasis psoriatic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Methotrexate is commonly prescribed for a variety of diseases including rheumatoid arthritis. For years standard medication with Methotrexate MTX has been suspected of either. Question addressed by the study Methotrexate MTX is a key anchor drug for rheumatoid arthritis RA management.
Organizing pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia or BOOP acute. For years standard medication with Methotrexate MTX has been suspected of either. Methotrexate has frequently been implicated as a causative agent in interstitial lung disease. Occasionally its use has been associated with diffuse interstitial lung disease DILD development 1. While there is an association with MTX and RA-ILD it is now known to be coincidental and not causative with the underlying inflammatory process driving ILD. Organizing pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia or BOOP acute. Methotrexate use and risk of lung disease in psoriasis psoriatic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.



























Post a Comment for "Methotrexate Interstitial Lung Disease"