Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Treatment Guidelines
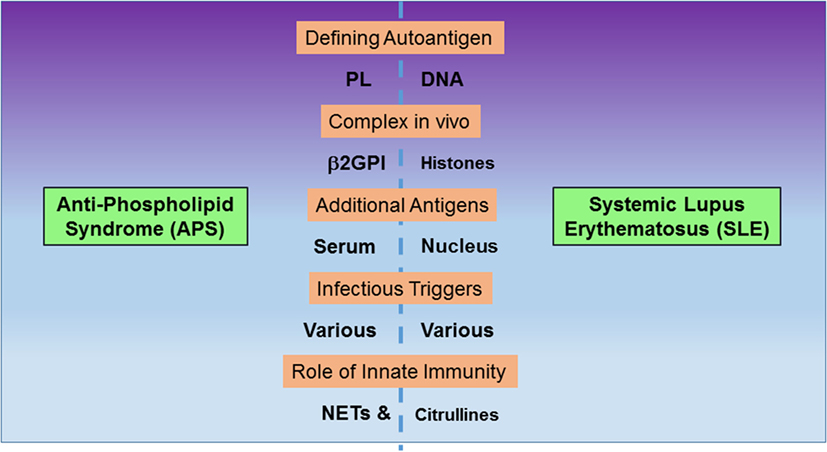
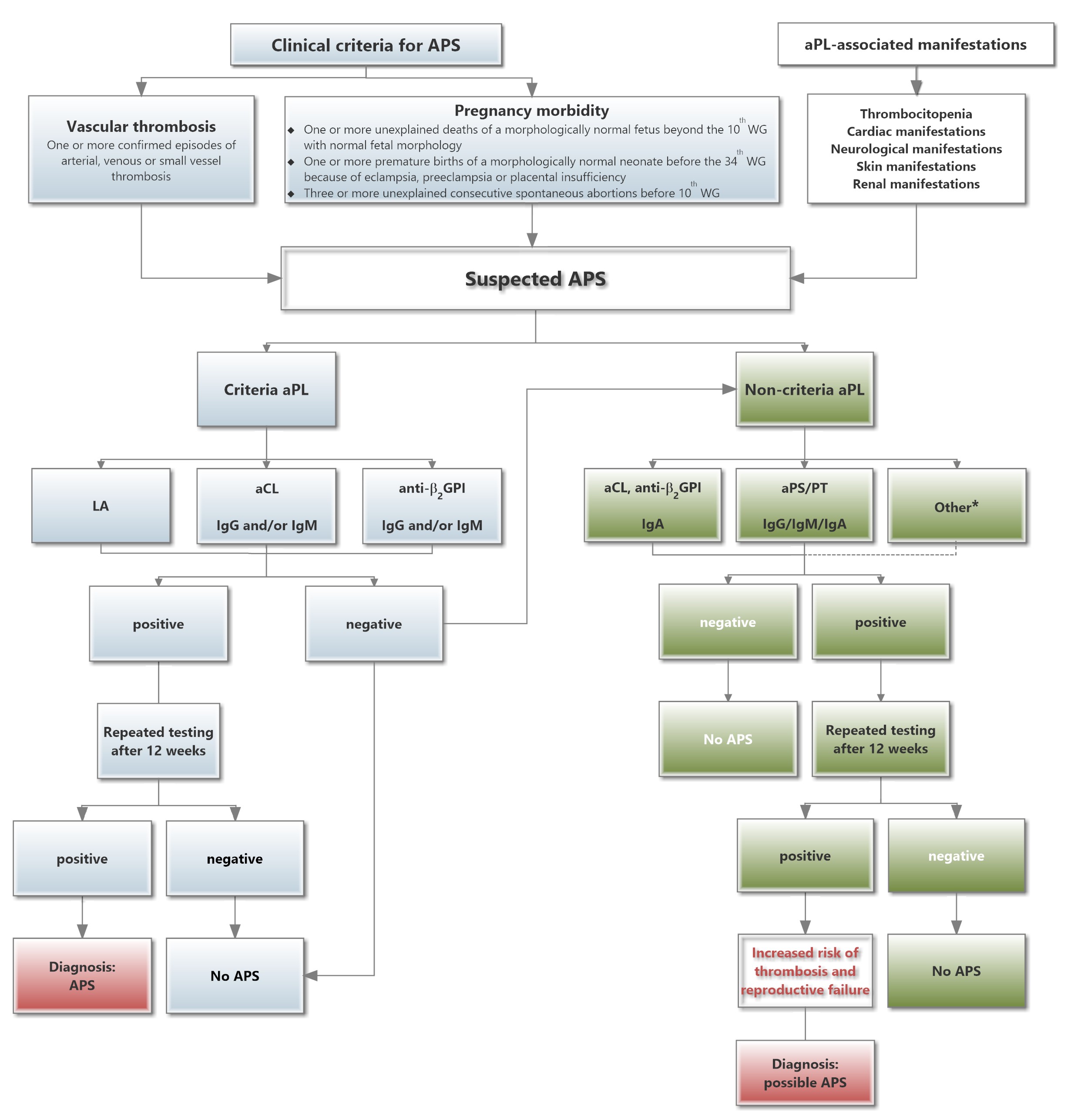
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome treatment guidelines. Antiphospholipid antibodies can induce endothelial-cell complement platelet neutrophil and monocyte activation leading to thrombosis renal failure heart valve disease pregnancy loss. Most patients with venous or arterial thrombosis and APS should receive conventional warfarin therapy administered to achieve an international normalized ratio INR range of 20-30. Antiphospholipid syndrome APS is a rare disease characterised by venous andor arterial thrombosis pregnancy complications and the presence of specific autoantibodies called antiphospholipid antibodies.
New guidelines for the treatment and management of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome have been established by the 13th International Committee on Antiphospholipid Antibodies. The major treatment issues in APS include the treatment of acute thromboembolic manifestations the choice of anticoagulation and the duration of anticoagulation. 80 unitskg intravenous bolus followed by 18 unitskghour infusion.
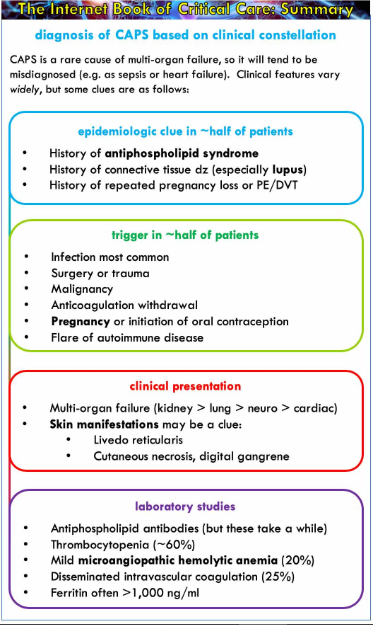
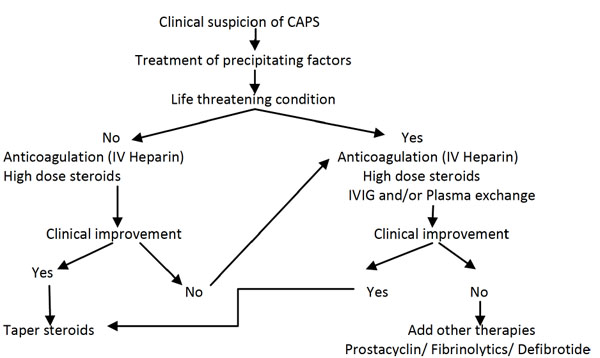
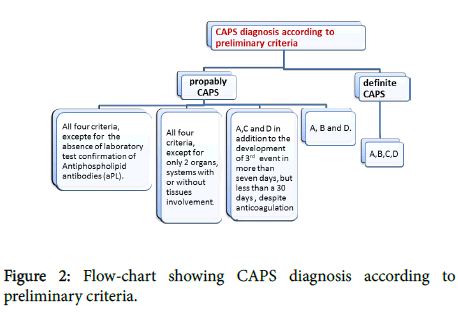
Early treatment is essential in catastrophic APS. The major treatment issues in APS include the treatment of acute thromboembolic manifestations the choice of anticoagulation and the duration of anticoagulation. Blood thinning works by stopping the blood clotting system working properly and prevents blood clots in patients with APS.
1 mgkg subcutaneously twice daily. Management of APS focuses on anticoagulation. A better understanding of the pathophysiology behind antiphospholipid antibody syndrome has led to novel approaches in the diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
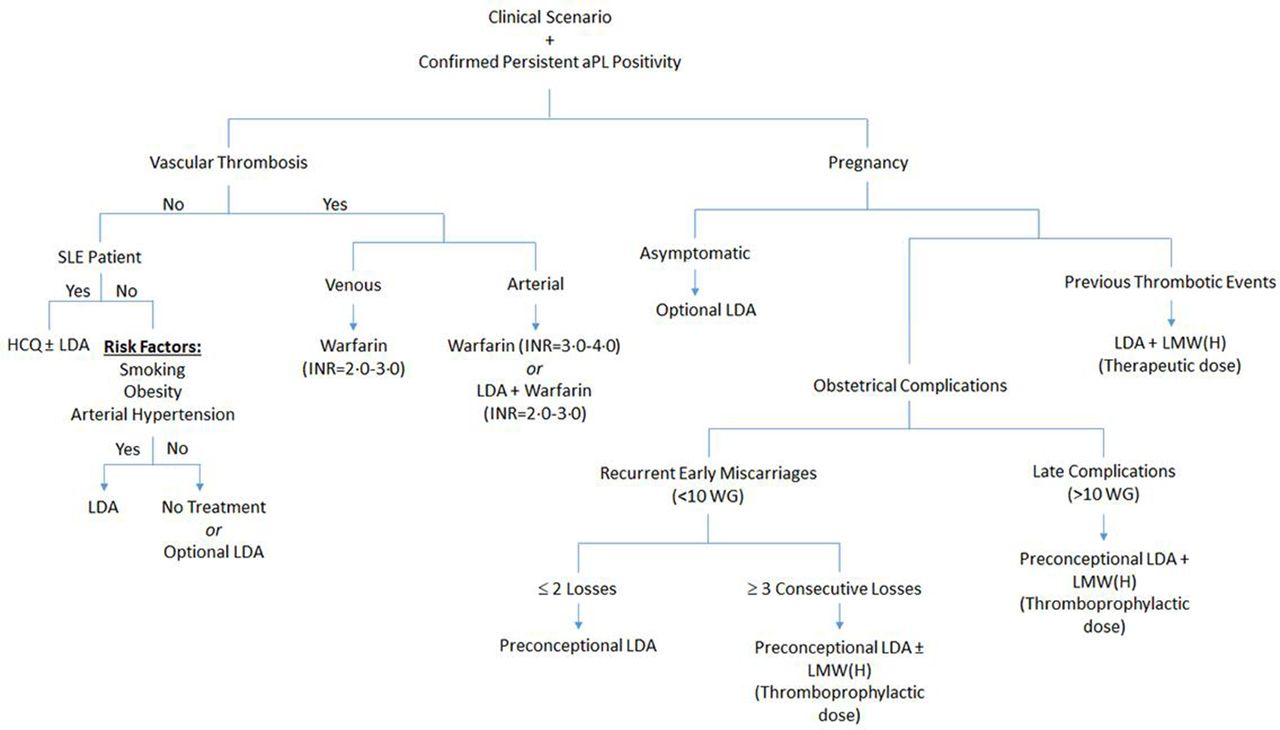
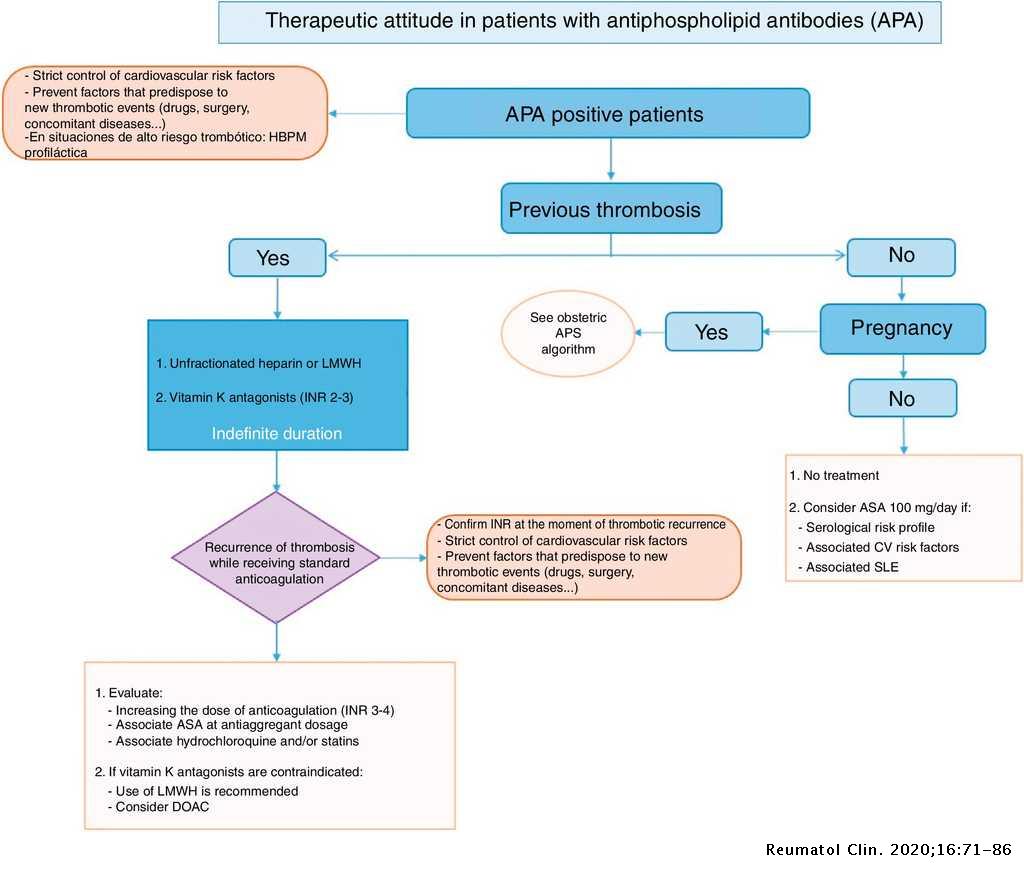
Other related issues include the prevention of first thrombosis among patients with aPL who do not meet criteria for APS. Adriana Danowski I. The 13th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies task force as well as current EULAR guidance recommend that patients with definite APS and a first venous event receive lifelong oral anticoagulation to a target INR of 2030.
Treatment of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome APS is a systemic autoimmune disease with thrombotic predilection resulting in vascular thrombotic events and obstetric complications. Intensity of anticoagulant therapy. In the most recent American College of Chest Physicians VTE treatment guidelines 14 patients with VTE are broadly divided into 3 major categories for the purposes of treatment considerations.
In patients with APS and first venous thrombosis after an initial therapy with unfractionated heparin UFH or LMWH and bridging therapy of heparin plus VKA treatment with VKA with a target INR of 23 is recommended. Alexandre Wagner Silva de Souza VII.
New guidelines for the treatment and management of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome have been established by the 13th International Committee on Antiphospholipid Antibodies.
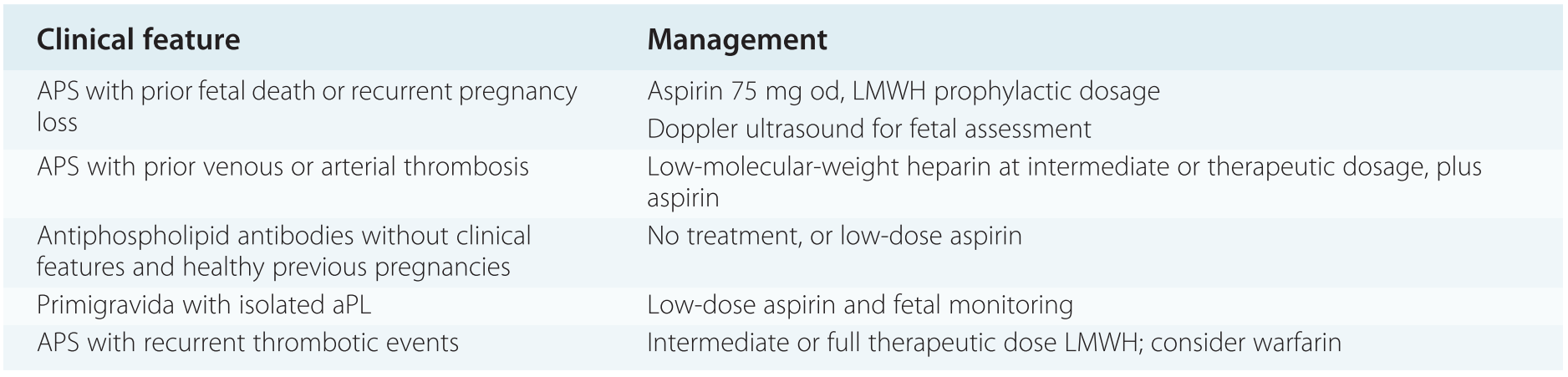
In patients with APS and first venous thrombosis after an initial therapy with unfractionated heparin UFH or LMWH and bridging therapy of heparin plus VKA treatment with VKA with a target INR of 23 is recommended. 80 unitskg intravenous bolus followed by 18 unitskghour infusion. Other related issues include the prevention of first thrombosis among patients with aPL who do not meet criteria for APS. Adriana Danowski I. Low-dose aspirin and therapeutic-dose heparin should be used in pregnant women with thrombotic APS regardless of the pregnancy history. Blood thinning works by stopping the blood clotting system working properly and prevents blood clots in patients with APS. In patients with APS and first venous thrombosis after an initial therapy with unfractionated heparin UFH or LMWH and bridging therapy of heparin plus VKA treatment with VKA with a target INR of 23 is recommended. A those with cancer b those in whom the VTE occurred in the setting of a reversible provoking risk factor ie surgery plaster cast immobilization estrogen therapy pregnancy prolonged 8 hours travel and c unprovoked ie absence of factors included in. Risk modification includes screening for and management of cardiovascular and venous thrombosis risk factors patient education about treatment adherence and lifestyle counselling.
Early treatment is essential in catastrophic APS. An acute episode of thrombosis should be managed the same as any other cause of thrombosis. Management of APS focuses on anticoagulation. A better understanding of the pathophysiology behind antiphospholipid antibody syndrome has led to novel approaches in the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Were formulated and voted. 1 mgkg subcutaneously twice daily. I Hospital Federal dos Servidores do Estado HFSE Rio de Janeiro RJ Brazil II Medical School Universidade Federal de Goiás.


























Post a Comment for "Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Treatment Guidelines"